Climate finance opportunities with the World Bank Group
The Canadian Trade Commissioner Service has more than 160 offices around the world with dedicated officers available to assist you with international trade activities. Specialized assistance is available for climate finance.
For information, contact Faheem.NoorAli@international.gc.ca
The World Bank (Washington D.C.)
The World Bank Group (WBG) is one of the largest sources of multilateral financing for developing countries and emerging markets around the world. The WBG consists of the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), the International Development Association (IDA), the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA), and the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). Canada is a member of all entities in the WBG. Sovereign-guaranteed lending is conducted through the IBRD, which lends to governments of middle- and low-income borrowing member countries (BMCs), and IDA, which provides interest-free loans and grants to BMC governments of poor countries. Supporting its goals of reducing poverty, increasing shared prosperity, and promoting sustainable development, in 2017 the IBRD and IDA committed US$42.1 billion in the form of credits, loans, grants and guarantees to BMCs across 394 operations.

Text version
| Agriculture, Fishing & Forestry (7%) |
| Education (7%) |
| Energy & Extractives (15 %) |
| Financial Sector (7%) |
| Health (6%) |
| Social Protection (10%) |
| Industry, Trade & Services (2%) |
| ICT (16%) |
| Public Administration (6%) |
| Transportation (14 %) |
| Water, Sanitation & Waste (10%) |
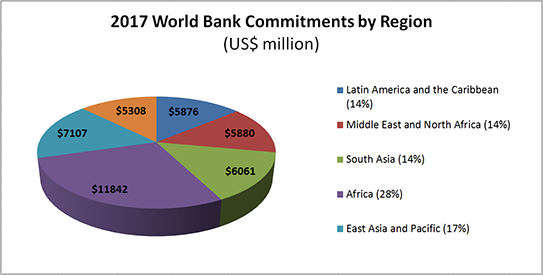
Text version
| Latin America and the Caribbean (14%) |
| Middle East and North Africa (14%) |
| South Asia (14%) |
| Africa (28%) |
| East Asia and Pacific (17%) |
| Europe and Central Asia (13%) |
Source: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/143021506909711004/World-Bank-Annual-Report-2017
Procurement processes
In 2015, the World Bank issued a new Procurement Framework and associated policies and procedures. Projects approved after July 1, 2016, are governed by procurement regulations. Prior to that date, the World Bank’s previous procurement framework applies. Responsible for project-related procurement, BMCs publicly post general procurement notices (GPNs), specific procurement notices (SPNs) and requests for expressions of interest (REOIs), and procurement opportunities are advertised on the World Bank’s Procurement website and on the UN's Development Business website. The World Bank carries out prior reviews of BMC procurement activities that are of high value and/or high risk, and conducts post-reviews to ensure compliance.
Procurement by member countries
Goods, works and services: BMCs are responsible for carrying out procurement activities financed by the World Bank. Larger contracts are usually subject to international competitive bidding (ICB). Prequalification is generally necessary for large/complex works, or where the high cost of preparing bids would discourage competition. The World Bank also requires BMCs to develop a project procurement strategy for development for each project financed, as well as a procurement plan. For consulting services, quality and cost-based selection is most often used.Procurement by the Bank
Corporate procurement: The World Bank’s corporate procurement team is responsible for the coordination and oversight of the Bank’s sourcing strategy, selection and contract execution for goods, services, construction and consulting services for the Bank. Information about the World Bank’s corporate procurement contract awards are available on its Corporate Procurement Contract Awards site. Vendors must complete a Vendor Registry Form to be eligible for a corporate procurement contract award.Private sector operations and finance
The World Bank Group’s non-sovereign-guaranteed Footnote 1 and private sector operations are conducted through the IFC and the MIGA. Companies seeking debt, equity or guarantees for private sector-led projects should refer to the IFC and the MIGA for additional information.
Climate finance
As part of its Climate Change Action Plan 2016-2020, the WBG has committed to increasing climate financing to 28% of its portfolio by 2020. In addition to directing its own capital toward low-carbon and climate-resilience support for BMCs, the World Bank acts as an intermediary for the Green Climate Fund, the Global Environment Facility and the Climate Investment Funds as these funds generally do not accept direct applications from the private sector. The World Bank also manages other climate-relevant donor trust funds. Complementing its existing climate financing mechanisms, the World Bank and the UN jointly developed the Invest4Climate convening platform to mobilize multiple sources of finance.